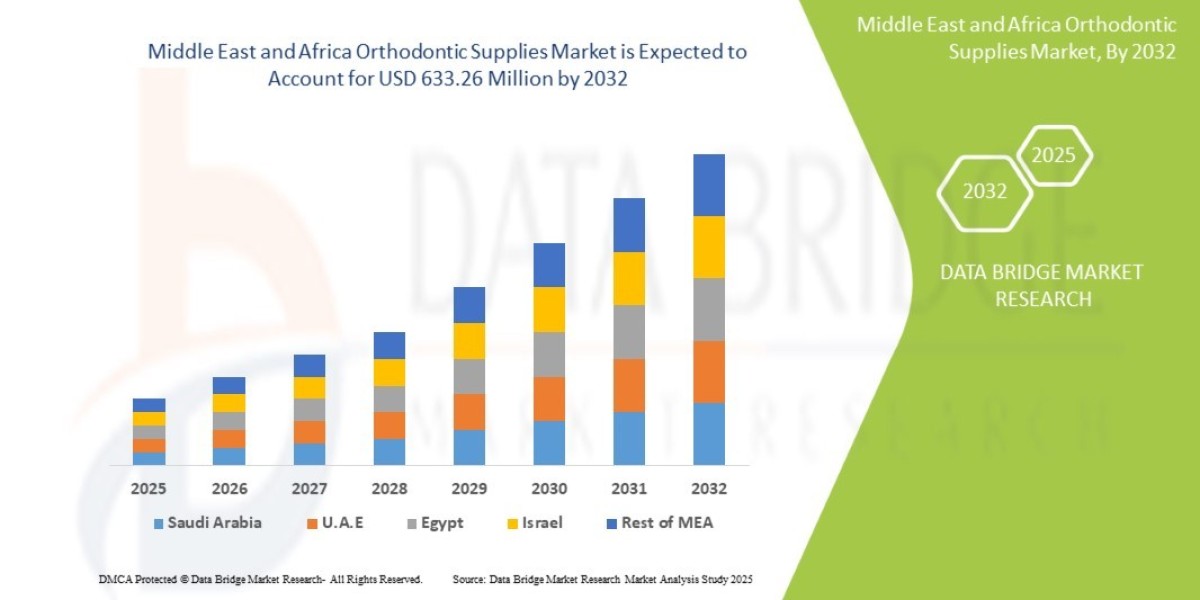
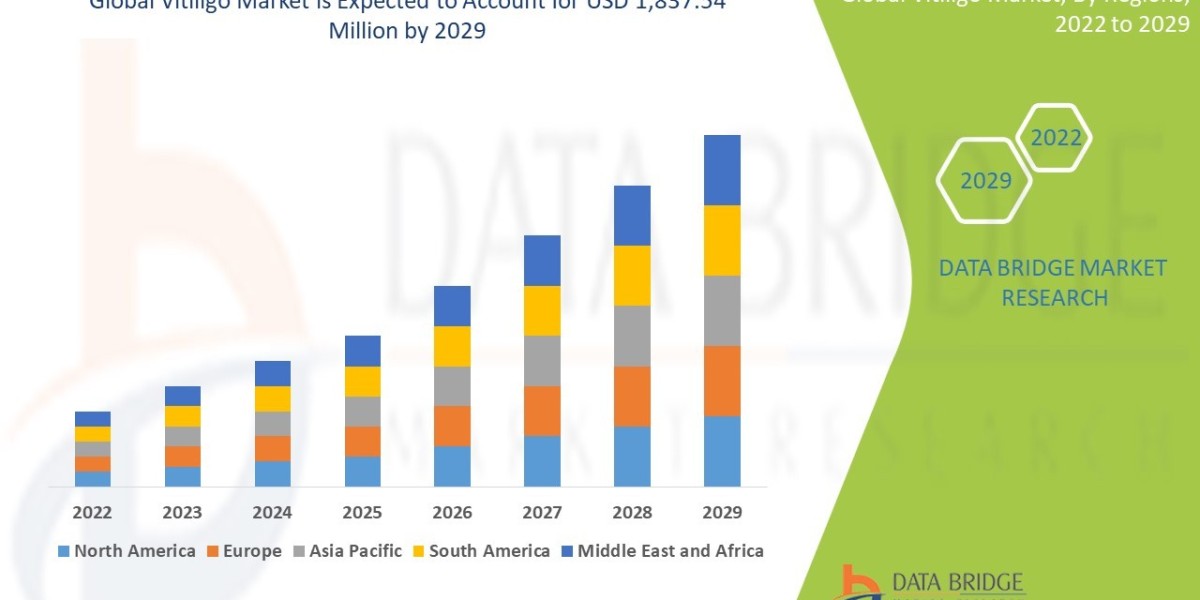
What is a Business Property Broker?

If you're wondering how to end up being a commercial property broker, this guide will stroll you through the steps to start your profession in this exciting field.
An industrial genuine estate broker is an intermediary in between sellers and purchasers of industrial realty, who assists clients offer, lease, or purchase industrial property. An industrial genuine estate broker can work as an independent agent, a company of commercial property agents, or as a member of an industrial genuine estate brokerage firm.
The primary distinction between an industrial genuine estate broker and an industrial real estate agent is that the previous can work independently while the latter does not. A commercial realty agent need to be employed by a licensed broker.
A residential or commercial property is classified as commercial real estate when it is just used for the function of performing business. Typically, industrial property is owned by an investor who gathers lease from each organization that runs from that residential or commercial property.
Examples of commercial real estate include office, strip shopping malls, hotels, corner store, and dining establishments. Sometimes, business realty is likewise owner-occupied, implying the organization that operates at the website is likewise the owner.
How to Become an Industrial Realty Broker: The Qualifications
Educational Requirements
The standard requirement for ending up being an industrial real estate broker is a high school diploma (or an equivalent academic certification). Most effective business genuine estate agents/brokers have an undergraduate or academic degree in business, statistics, finance, economics, or property (with an unique concentrate on the sale or lease of business residential or commercial property).
Legal Requirements
An industrial property broker is a realty expert who has actually continued their education beyond the level of a business realty agent. To be licensed as a business property broker, a private must acquire a state license in each state that they want to practice their profession in. A specific must pass the industrial realty broker examination in order to obtain the accreditation and a state license. (Note: A commercial property license is different from a real estate representative license).
The following actions must be carried out for a specific to be eligible to take the business realty broker test:
- The individual must be utilized with a company for a minimum of one to 3 years (differs by state).
- Next, they are required to take 60-90 hours of state-approved licensing courses.
- After the conclusion of the state-approved licensing courses, the person is then eligible to take the exam. As part of the test, candidates are typically quizzed about dominating federal and state laws in the industrial property industry.
Those who pass the examination are certified as commercial genuine estate brokers. To continue holding a business real estate broker license, a business property broker must take appropriate continuing education courses every 2 to four years (again, the specific requirements vary from state to state - if you run in several states, you need to pass the requirements of the strictest state). Popular and practical continuing education courses consist of mortgage loan brokering, property appraisal, and real estate law.
Compensation of a Commercial Realty Broker
The earnings of a commercial realty broker is based on the commissions produced by sales. The listing contract (a contract between the listing broker and the seller defining information of the listing) mentions the broker's commission. The brokerage commission for commercial realty is flexible and, usually, is about 6% of the last list price. If the residential or commercial property is being rented instead of offered, then the brokerage fee is picked the basis of square footage and net rental earnings.

Usually, the commission is paid by the seller from the sale continues unless the seller and buyer work out a split (Note: the seller frequently factors the commission into the asking cost). The commission is paid when the offer is closed. The commission is divided between the purchasing broker and the selling/listing broker.
However, if the broker is not working separately, the commission is split four ways. First, the commission is divided and credited with the purchasing broker and listing broker. Each broker then takes their broker fee/commission and, out of that, pays the suitable representative their commission, which is generally a flat fee per deal carried out.
The following costs need to be taken into consideration when setting the brokerage commission:
- Association costs.
- Licensing costs.
- Advertising and marketing costs.
- Multiple Listing Service (MLS) fees
A credible reputation, repeat organization, a strong local economy, and high-priced sales result in higher commissions for commercial real estate brokers.
Advantages of Hiring an Industrial Property Broker

An industrial real estate broker can assist prospective clients save money and time by carrying out the following functions:
Building a network in the target neighborhood: In each area that a business realty broker intends to work in, they create a network with important members of the worried community. This makes sure that they have a first mover's advantage each time a residential or commercial property is up for sale or when a potential buyer emerges in the neighborhood.
Understanding tax and zoning laws: Many individuals avoid buying industrial property because of the a great deal of complex rules and policies governing the taxation and purchase of commercial residential or commercial property. This complexity is compounded by the reality that these rules and regulations differ across states, industries, and zones. An industrial property broker should have an excellent understanding of tax and zoning laws to complete the aforementioned rules on their client's behalf and, therefore, get rid of a barrier to investment in industrial realty.
Evaluating service strategies: A business property broker examines their customers' organization strategies to determine their feasibility. They typically utilize statistical analysis (such as break-even analysis) to identify the standard margin of security on a client's investment.
Negotiating with clients: Commercial real estate brokers need to be outstanding mediators and arbitrators because, unlike domestic property brokers, industrial real estate brokers frequently need to handle more than two celebrations when organizing the sale or lease of a residential or commercial property. The numerous celebrations frequently have conflicting incentives, which a commercial property representative helps align through settlements. An industrial genuine estate broker should have outstanding interaction and persuasion abilities to effectively browse settlements.
Conducting research: Often, the success of a customer's organization depends upon local conditions. A commercial property broker needs to provide prospective purchasers of business real estate with research study concerning regional demographics, services, environmental quality, residential or commercial property maintenance expenses, and the desirability of the area of the residential or commercial property.

Analyzing lease payments: An industrial realty broker investigates and examines trends in lease payments for industrial property in the area in which she/he operates. There are four standard types of commercial property leases:
1. Single net lease: Under this lease, residential or commercial property tax is paid by the renter.
2. Double-net (NN) lease: Under this lease, residential or commercial property tax and insurance coverage are paid by the occupant.
3. Triple-net (NNN) lease: Under this lease, residential or commercial property tax, insurance, and upkeep are paid by the occupant.
4. Gross lease: Under this lease, residential or commercial property tax, insurance coverage, and upkeep is paid by the property manager. The renter only pays rent.
Larger occupants generally enter into longer leases, which supplies security to the property owner as a consistent stream of rental earnings is ensured. (For instance, a business such as Amazon is unlikely to lease office or warehousing area that it plans to inhabit for just one year.) However, lease rents can be adjusted in a more versatile way under a much shorter lease term.
For more information about checking out an industrial lease, consider CFI's course on How to Read a Lease & Analyze a Lease Roll.

Disadvantages of Hiring an Industrial Real Estate Broker
Under some scenarios, an industrial property broker might reveal a customer just those residential or commercial properties where the commission is high, advise a client to negotiate paying rent higher than necessary, or rush the client through the process in order to maximize the variety of deals that he/she can make. To counter such habits, the customer can enter a contract with the broker in which the latter is paid a flat cost as opposed to a commission.
Common Metrics Used by Commercial Property Brokers
Gross Rental Yield: Gross rental yield expresses rental earnings as a portion of the worth of the residential or commercial property before taxes and other costs are deducted. It is computed as follows:
Gross Rental Yield = (Annual Rental Income/Cost of Residential Or Commercial Property) x 100
Commercial realty leads to an average yield of 7% -7.5%, instead of domestic realty, which results in a typical yield of 4% -5%. This is a popular metric for comparing industrial genuine estate residential or commercial properties that are going to be leased/ leased out.
Capital Gain/Total Return on Investment: Capital gain refers to the profit made by selling a residential or commercial property. It is determined as follows:
Total Roi = (Gain from Investment - Expense of Investment)/ Expense of Investment) x 100
This is a popular metric for comparing industrial real estate residential or commercial properties that are going to be sold. Investment in industrial real estate, which supplies a wide scope for improvement and/or expansion, is ideal for making capital gains.
However, it is essential to note that there exists an inverted relationship between gross rental yield and capital gain/total return on financial investment.
Find out more
Thank you for checking out CFI's guide to an industrial real estate broker. Commercial brokers are essential for a healthy residential or commercial property market.